BR24G04FJ-3 データシートの表示(PDF) - ROHM Semiconductor
部品番号
コンポーネント説明
メーカー
BR24G04FJ-3 Datasheet PDF : 37 Pages
| |||
BR24G04-3
Datasheet
Timing Chart
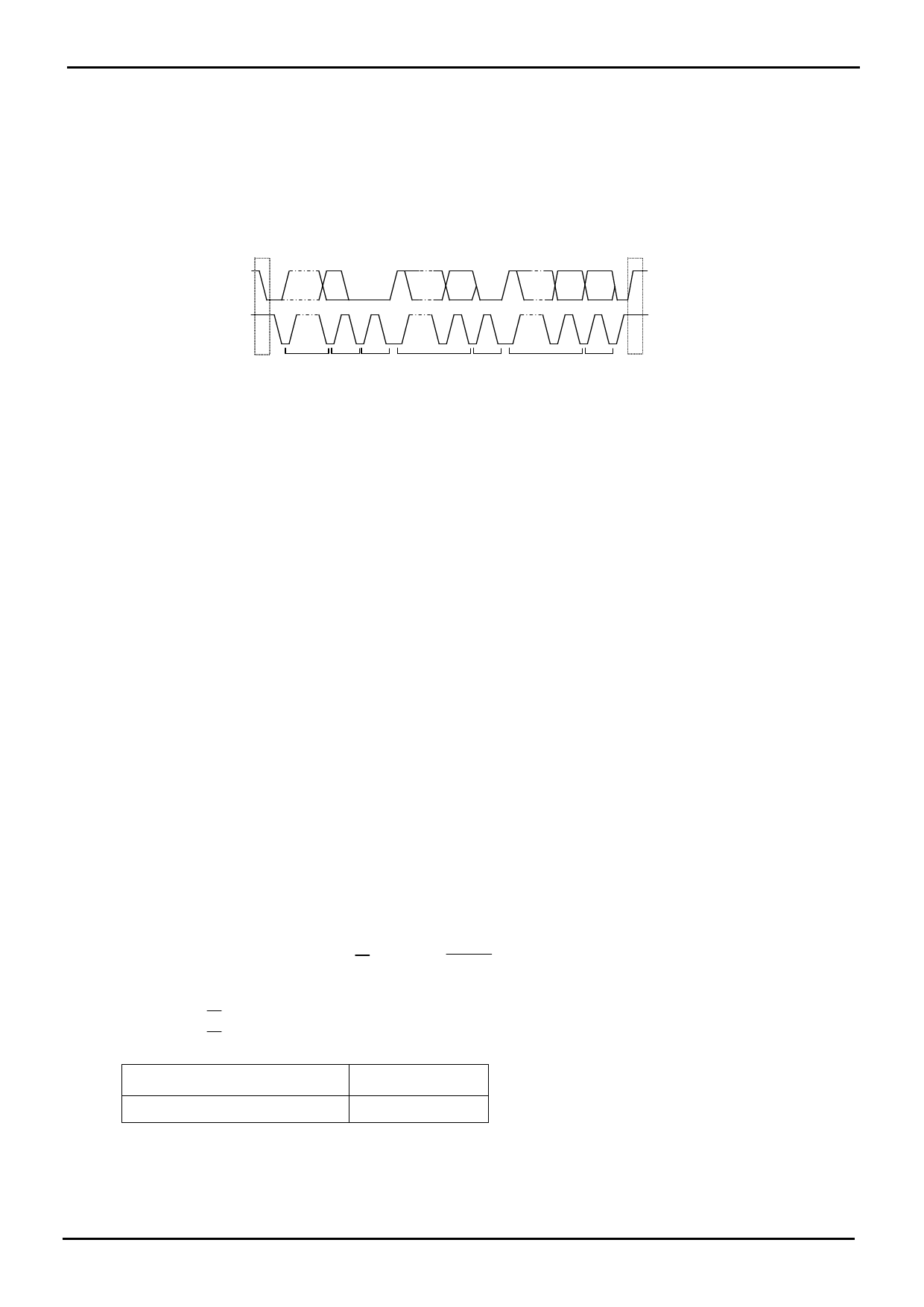
1. I2C BUS Data Communication
I2C BUS data communication starts by start condition input, and ends by stop condition input. Data is always 8bit long,
and acknowledge is always required after each byte. I2C BUS data communication with several devices is possible by
connecting with 2 communication lines: serial data (SDA) and serial clock (SCL).
Among the devices, there should be a “master” that generates clock and control communication start and end. The
rest become “slave” which are controlled by an address peculiar to each device, like this EEPROM. The device that
outputs data to the bus during data communication is called “transmitter”, and the device that receives data is called
“receiver”.
SDA
1-7
8
9
1-7
8
9
1-7
8
SCL
S
START ADDRESS
condition
R/W ACK
DATA
ACK
DATA
Figure 34. Data Transfer Timing
9
P
ACK STOP
condition
2. Start Condition (Start Bit Recognition)
(1) Before executing each command, start condition (start bit) where SDA goes from 'HIGH' down to 'LOW' when
SCL is 'HIGH' is necessary.
(2) This IC always detects whether SDA and SCL are in start condition (start bit) or not, therefore, unless this
condition is satisfied, any command cannot be executed.
3. Stop Condition (Stop Bit Recognition)
(1) Each command can be ended by a stop condition (stop bit) where SDA goes from 'LOW' to 'HIGH' while SCL is
'HIGH'.
4. Acknowledge (ACK) Signal
(1) The acknowledge (ACK) signal is a software rule to show whether data transfer has been made normally or not.
In a master-slave communication, the device (Ex. µ-COM sends slave address input for write or read command,
to this IC ) at the transmitter (sending) side releases the bus after output of 8bit data.
(2) The device (Ex. This IC receives the slave address input for write or read command from the µ-COM) at the
receiver (receiving) side sets SDA 'LOW' during the 9th clock cycle, and outputs acknowledge signal (ACK
signal) showing that it has received the 8bit data.
(3) This IC, after recognizing start condition and slave address (8bit), outputs acknowledge signal (ACK signal)
'LOW'.
(4) After receiving 8bit data (word address and write data) during each write operation, this IC outputs acknowledge
signal (ACK signal) 'LOW'..
(5) During read operation, this IC outputs 8bit data (read data) and detects acknowledge signal (ACK signal) 'LOW'.
When acknowledge signal (ACK signal) is detected, and stop condition is not sent from the master (µ-COM)
side, this IC continues to output data. When acknowledge signal (ACK signal) is not detected, this IC stops data
transfer, recognizes stop condition (stop bit), and ends read operation. Then this IC becomes ready for another
transmission.
5. Device Addressing
(1) Slave address comes after start condition from master.
(2) The significant 4 bits of slave address are used for recognizing a device type.
The device code of this IC is fixed to '1010'.
(3) Next slave addresses (A2 A1 --- device address) are for selecting devices, and plural ones can be used on a
same bus according to the number of device addresses.
(4) The most insignificant bit ( R / W --- READ/ WRITE ) of slave address is used for designating write or read
operation, and is as shown below.
Setting R / W to 0 ------- write (setting 0 to word address setting of random read)
Setting R / W to 1 ------- read
Slave Address
1 0 1 0 A2 A1 P0 R/―W―
P0 is page select bit.
Maximum number of
Connected buses
4
www.rohm.com
©2013 ROHM Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
TSZ22111・15・001
13/33
TSZ02201-0R2R0G100180-1-2
28.Mar.2017 Rev.005