SAA2500H データシートの表示(PDF) - Philips Electronics
部品番号
コンポーネント説明
メーカー
SAA2500H Datasheet PDF : 47 Pages
| |||
Philips Semiconductors
MPEG Audio Source Decoder
Preliminary specification
SAA2500
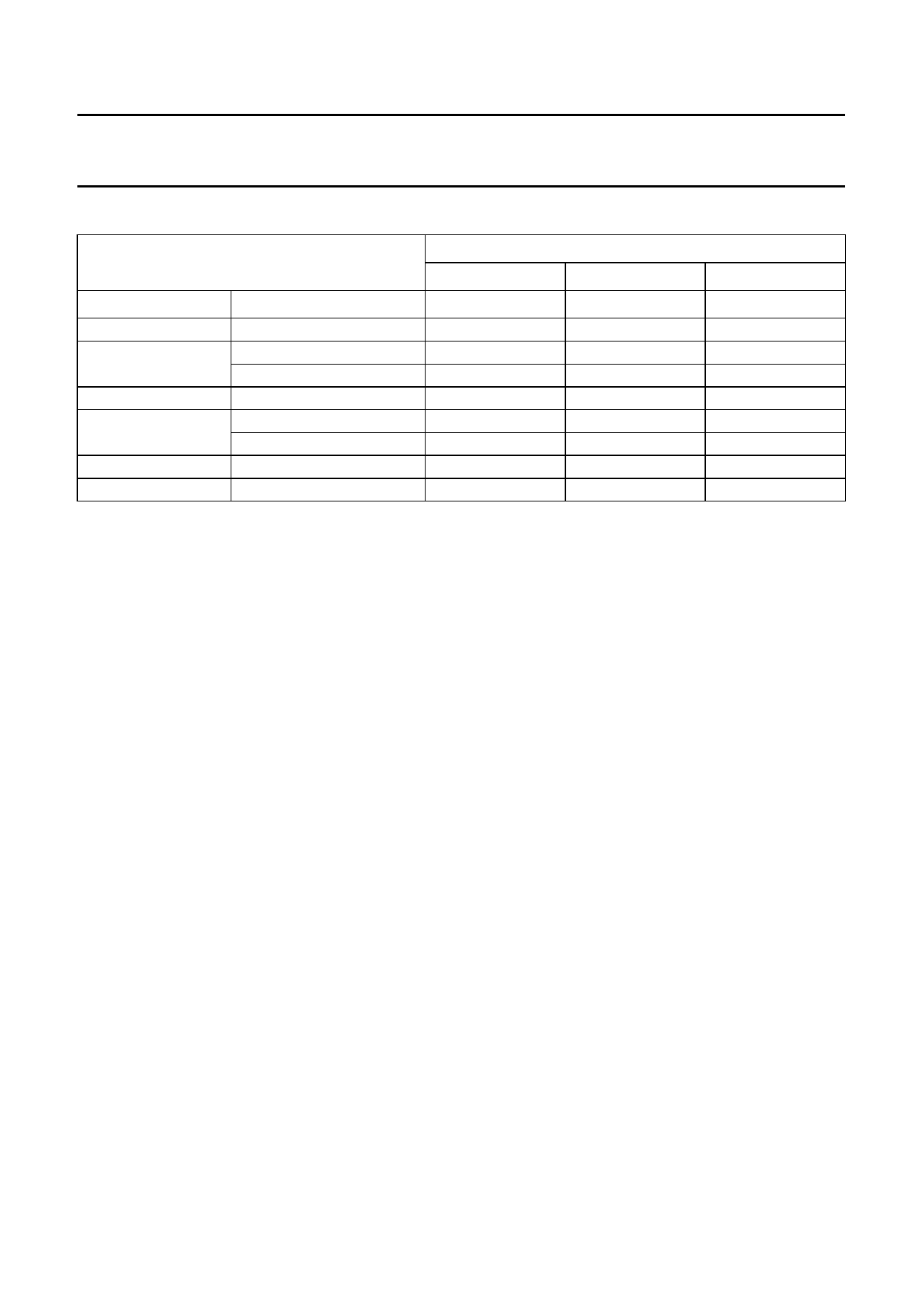
Table 2 Target applications.
ATTRIBUTE CONDITIONS
INPUT INTERFACE
FSCLKM
MCLKIN
X22IN
FSCLKIN
FSCLK
Remarks
CONDITIONS
MCLK24 = 1
MCLK24 = 0
FSCLK384 = 1
FSCLK384 = 0
FCKENA = 1 (L3)
S
SLAVE INPUT
X
24.576 MHz
12.288 MHz
note 1
384fs
256fs
copy of FSCLKIN
note 2
APPLICATION
M0
MASTER INPUT
0
24.576 MHz
illegal
22.579 MHz
illegal
note 1
256fs
note 3
M1
MASTER INPUT
1
24.576 MHz
12.288 MHz
note 1
384fs
256fs
copy of FSCLKIN
−
Notes
1. Must be electrically defined; e.g.: LOW.
2. FSCLKIN must be locked to input data clock CDSCL; see Section “The coded data slave input interface”.
3. FSCLKIN is not used, but FSCLK384 must be LOW.
Sections “Clock frequencies when using the slave
input” and “Clock frequencies when using the master
input” explain which clock sources are activated by the
SAA2500 depending on the selected input interface. This
automatic clock source selection makes it easy to apply
the SAA2500 in systems with two ISO/MPEG coded data
sources (one connected to the master input, an one to the
slave input), even if these data sources use different
clocks.
Buffered clock outputs
The SAA2500 provides a signal MCLK which is a buffered
version of MCLKIN. MCLK can be set to 3-state by setting
the L3 control interface flag MCKDIS to 1 in applications
where MCLK is not needed.
Signal FSCLK is copied from the FSCLKIN input for
application types S and M1 or generated with a frequency
of 256fs by the SAA2500 for application type M0. After a
device reset, FSCLK must be enabled explicitly by setting
L3 flag FCKENA, or can alternatively be left 3-stated in
applications where it is not needed.
After a device reset, MCLK is enabled; FSCLK is disabled
(i.e. both MCKDIS and FCKENA are set to 0).
Functionality issues
The SAA2500 fully complies with ISO/MPEG layer I and II
with the slave input. With the master input, the SAA2500
complies with ISO/MPEG layer I and II, excluding the free
format bit rate. Several aspects of the decoding process,
as well as the audio post-processing features, offered by
the SAA2500, are described in more detail below.
Synchronization to input data bitstreams
After a reset, the SAA2500 mutes both sub band and
baseband audio data. After data inputting has started, the
SAA2500 searches either for a sync pattern or a sync
pulse. The speed at which input data is read by the master
input to search for synchronisation is described below. If
the application is such that the SAA2500 starts at a
random moment in time compared to the bitstream,
maximal one frame is skipped before a synchronisation
pattern or pulse is encountered.
When the SAA2500 has detected the first synchronisation
word or pulse, a number of frames are decoded in order to
verify synchronisation; the input data for these frames is
read and decoded, but meanwhile the audio output is
muted. The number of muted frames depends on whether
the ISO/MPEG CRC is active, and whether the bit rate is
free format. If the synchronisation is found to be false, the
SAA2500 resumes the initial synchronisation as described
above. If the detected pulse/pattern is concluded to be a
real synchronisation pulse/pattern, Table 3 indicates the
number of muted frames.
September 1994
9