AD9802 データシートの表示(PDF) - Analog Devices
部品番号
コンポーネント説明
メーカー
AD9802 Datasheet PDF : 20 Pages
| |||
AD9802
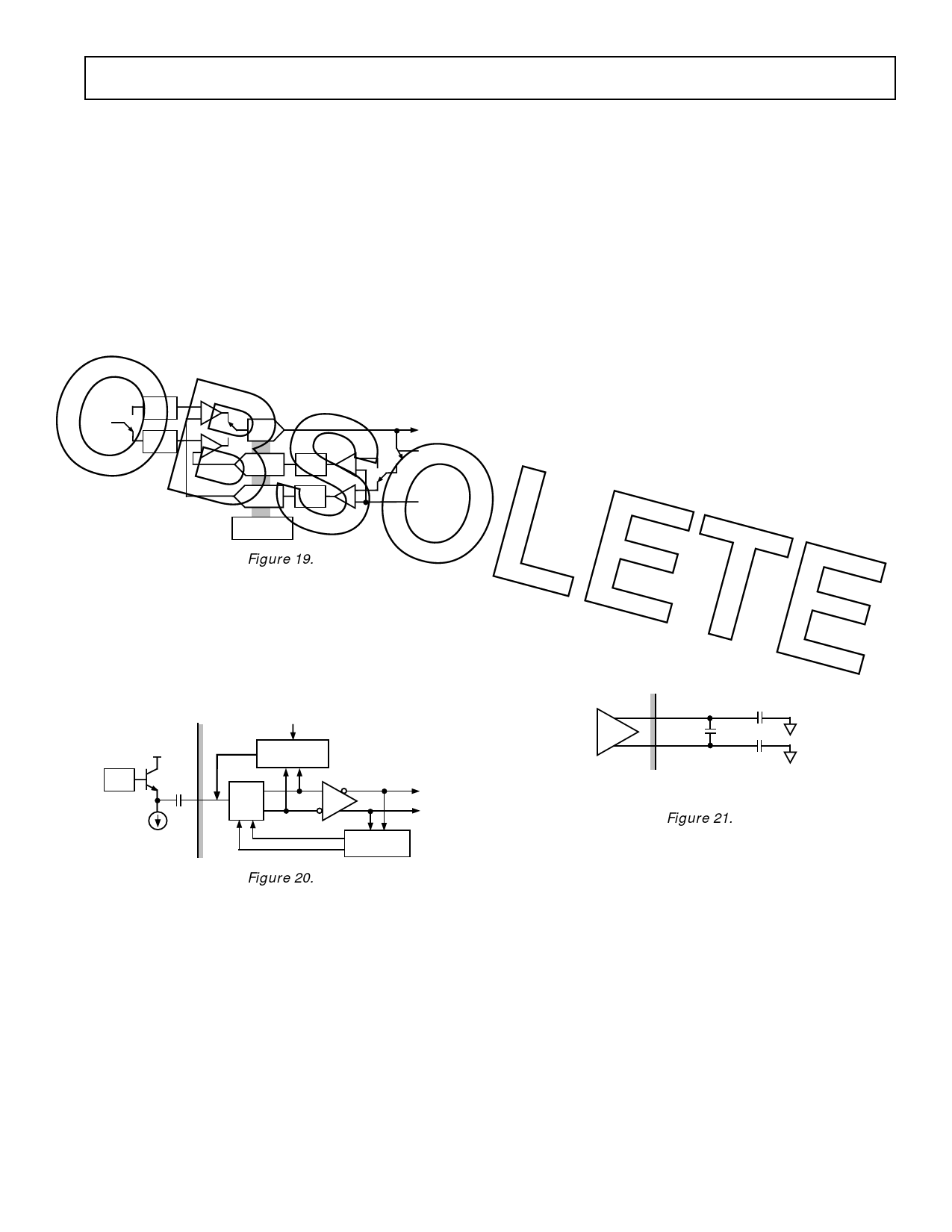
The actual implementation of this loop is slightly more compli- To avoid problems associated with processing these transients,
cated as shown in Figure 19. Because there are two separate
the AD9802 includes an input blanking function. When active
CDS blocks, two black level feedback loops are required and
(PBLK = LOW) this function stops the CDS operation and
two offset voltages are developed. Figure 19 also shows an addi- allows the user to disconnect the CDS inputs from the CCD
tional PGA block in the feedback loop labeled “RPGA.” The
buffer.
RPGA uses the same control inputs as the PGA, but has the
inverse gain. The RPGA functions to attenuate by the same
factor as the PGA amplifies, keeping the gain and bandwidth of
the loop constant.
If the input voltage exceeds the supply rail by more than 0.3 V,
then protection diodes will be turned on, increasing current flow
into the AD9802 (see Equivalent Input Circuits). Such voltage
levels should be externally clamped to prevent device damage or
There exists an unavoidable mismatch in the two offset voltages reliability degradation.
used to correct both CDS blocks. This mismatch causes a slight 10-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
difference in the offset level for odd and even pixels, called
The ADC employs a multibit pipelined architecture that is
OBSOLETE “pixel-to-pixel offset” (see Specifications). The pixel-to-pixel
offset is an output referred specification, because the black level
correction is done using the output of the PGA.
CDS1
IN
CDS2
PGA
RPGA2 INT2
ADC
CLPOB
RPGA1 INT1
NEG REF
CONTROL
Figure 19.
Input Bias Level Clamping
The buffered CCD output is connected to the AD9802 through
an external coupling capacitor. The dc bias point for this cou-
pling capacitor is established during the clamping (CLPDM =
well suited for high throughput rates while being both area and
power efficient. The multistep pipeline presents a low input
capacitance resulting in lower on-chip drive requirements. A
fully differential implementation was used to overcome head-
room constraints of the single +3 V power supply.
Direct ADC Input
The analog processing circuitry may be bypassed in the
AD9802. When ADCMODE (Pin 41) is taken high, the
ADCIN pin provides a direct input to the SHA. This feature
allows digitization of signals that do not require CDS and
gain adjustment. The PGA output is disconnected from the
SHA when ADCMODE is taken high.
Differential Reference
The AD9802 includes a 0.5 V reference based on a differential,
continuous-time bandgap cell. Use of an external bypass capaci-
tor reduces the reference drive requirements, thus lowering the
power dissipation. The differential architecture was chosen for
LOW) period using the “dummy clamp” loop shown in Figure
its ability to reject supply and substrate noise. Recommended
20. When closed around the CDS, this loop establishes the
decoupling shown in Figure 21.
desired dc bias point on the coupling capacitor.
CLPDM
INPUT
CLAMP
REF
VRT
VRB
0.1F
1F
0.1F
CCD
CDS
PGA
TO ADC
Figure 21.
BLACK
LEVEL CLP
Figure 20.
Input Blanking
In some applications, the AD9802’s input may be exposed to
large signals from the CCD. These signals can be very large,
relative to the AD9802’s input range, and could thus saturate
on-chip circuit blocks. Recovery time from such saturation
conditions could be substantial.
Internal Timing
The AD9802’s on-chip timing circuitry generates all clocks
necessary for operation of the CDS and ADC blocks. The user
needs only to synchronize the SHP and SHD clocks with the
CCD waveform, as all other timing is handled internally. The
ADCCLK signal is used to strobe the output data, and can be
adjusted to accommodate desired timing.
REV. 0
–9–