RF3198 データシートの表示(PDF) - RF Micro Devices
部品番号
コンポーネント説明
メーカー
RF3198 Datasheet PDF : 16 Pages
| |||
RF3198
Theory of Operation
Overview
The RF3198 is a dual-band EGSM900 and DCS1800 power amplifier module that incorporates an indirect closed loop method
of power control. This simplifies the phone design by eliminating the need for the complicated control loop design. The indirect
closed loop appears as an open loop to the user and can be driven directly from the DAC output in the baseband circuit.
Theory of Operation
The indirect closed loop is essentially a closed loop method of power control that is invisible to the user. Most power control
systems in GSM sense either forward power or collector/drain current. The RF3198 does not use a power detector. A high-
speed control loop is incorporated to regulate the collector voltage of the amplifier while the stage are held at a constant bias.
The VRAMP signal is multiplied by a factor of 2.65 and the collector voltage for the second and third stages are regulated to the
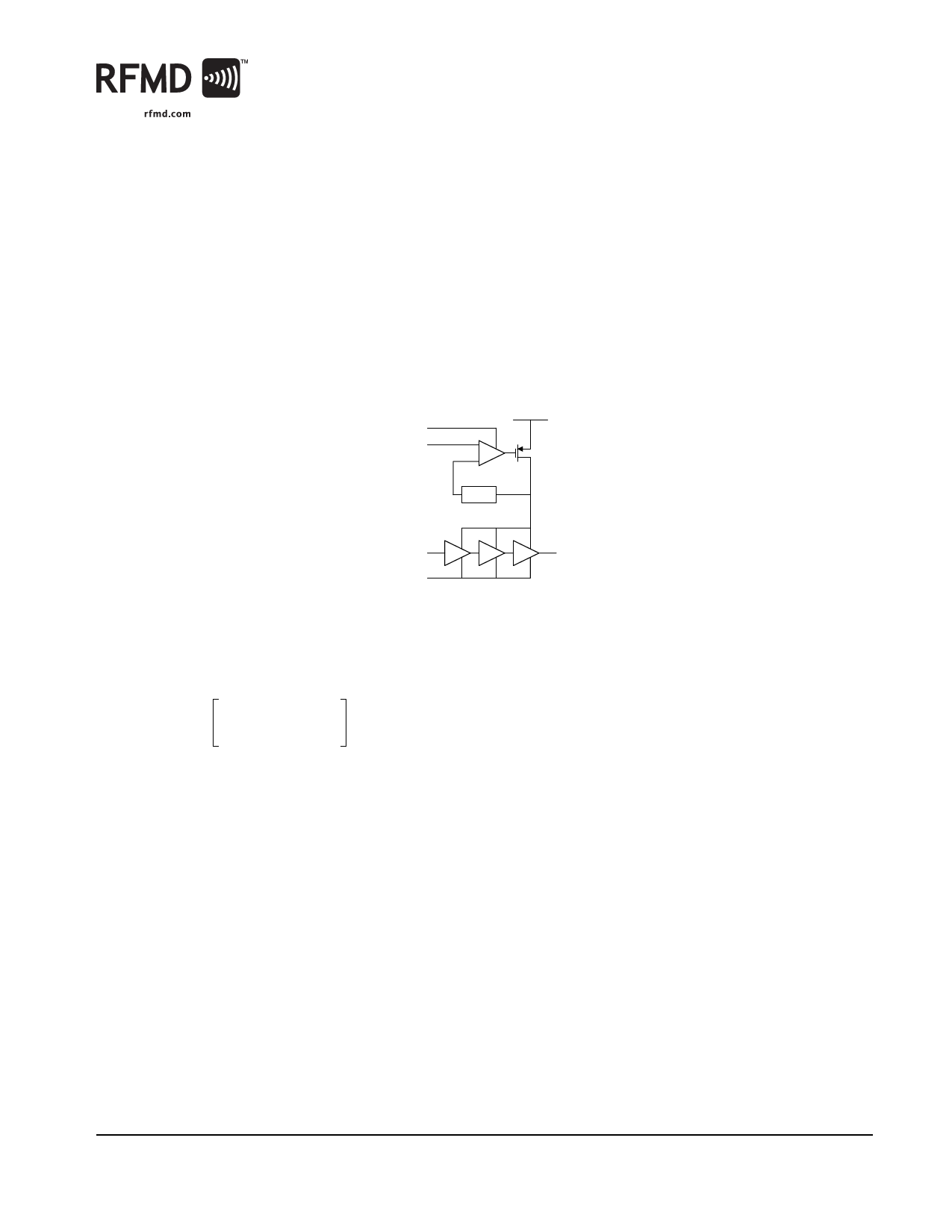
multiplied VRAMP voltage. The basic circuit is shown in the following diagram.
TX ENABLE
VRAMP
VBATT
H(s)
RF IN
RF OUT
TX ENABLE
By regulating the power, the stages are held in saturation across all power levels. As the required output power is decreased
from full power down to 0dBm, the collector voltage is also decreased. This regulation of output power is demonstrated in
Equation 1 where the relationship between collector voltage and output power is shown. Although load impedance affects out-
put power, supply fluctuations are the dominate mode of power variations. With the RF3198 regulating collector voltage, the
dominant mode of power fluctuations is eliminated.
PdBm
=
10 ⋅ log
-(--2----⋅---V----C----C----–-----V----S---A---T---)--2-
8 ⋅ RLOAD ⋅ 10–3
(Eq. 1)
There are several key factors to consider in the implementation of a transmitter solution for a mobile phone. Some of them are:
• Current draw and system efficiency
• Power variation due to Supply Voltage
• Power variation due to frequency
• Power variation due to temperature
• Input impedance variation
• Noise power
• Loop stability
• Loop bandwidth variations across power levels
• Burst timing and transient spectrum trade offs
• Harmonics
Rev A0 DS070801
7628 Thorndike Road, Greensboro, NC 27409-9421 · For sales or technical
support, contact RFMD at (+1) 336-678-5570 or sales-support@rfmd.com.
11 of 16