ACPL-P456-500E データシートの表示(PDF) - Broadcom Corporation
部品番号
コンポーネント説明
メーカー
ACPL-P456-500E
ACPL-P456-500E Datasheet PDF : 14 Pages
| |||
ACPL-P456 and ACPL-W456
Data Sheet
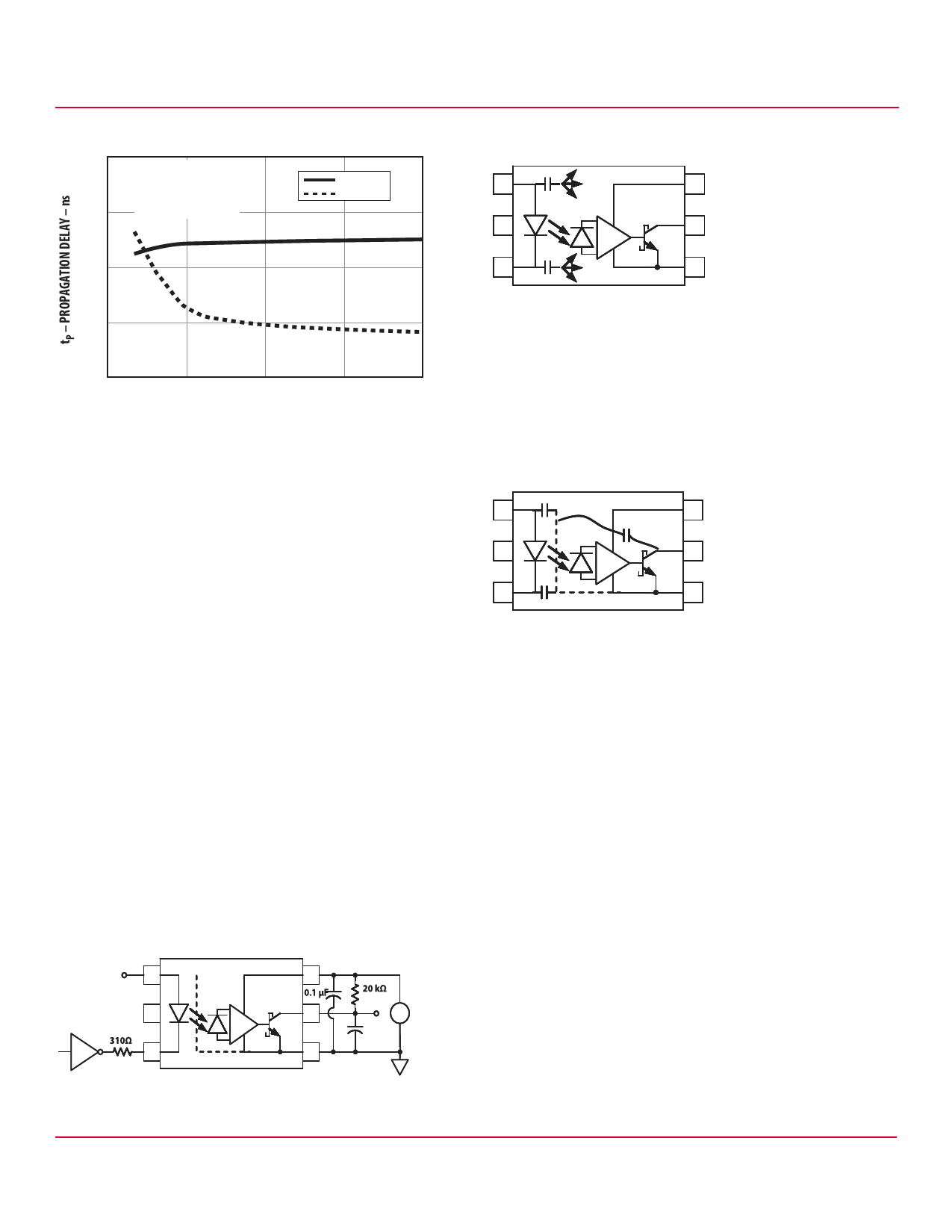
Figure 11 Propagation Delay vs. Input Current
500
VCC = 15V
CL = 100 pF
RL = 20 kΩ
tPLH
tPHL
400
TA = 25°C
Figure 13 Optocoupler Input to Output Capacitance Model for
Unshielded Optocouplers
1 CLEDP
6
2
5
300
3 CLEDN
4
200
100
0
5
10
15
20
IF – FORWARD LED CURRENT – mA
Applications Information
LED Drive Circuit Considerations For Ultra High
CMR Performance
Without a detector shield, the dominant cause of optocoupler
CMR failure is capacitive coupling from the input side of the
optocoupler, through the package, to the detector IC as shown
in Figure 13. The ACPL-P456/W456 improve CMR performance
by using a detector IC with an optically transparent Faraday
shield, which diverts the capacitively coupled current away
from the sensitive IC circuitry. However, this shield does not
eliminate the capacitive coupling between the LED and the
optocoupler output pin and output ground as shown in
Figure 14. This capacitive coupling causes perturbations in the
LED current during common mode transients and becomes the
major source of CMR failures for a shielded optocoupler. The
main design objective of a high CMR LED drive circuit becomes
keeping the LED in the proper state (on or off ) during common
mode transients. For example, the recommended application
circuit (Figure 12), can achieve 15 kV/μs CMR while minimizing
component complexity. Note that a CMOS gate is
recommended in Figure 12 to keep the LED off when the gate
is in the high state.
Figure 12 Recommended LED Drive Circuit
+5V
1
2
3
CMOS
SHIELD
6
5
VOUT +
-
VCC = 15V
CL*
4
* 100 pF TOTAL
CAPACITANCE
Another cause of CMR failure for a shielded optocoupler is
direct coupling to the optocoupler output pins through
CLEDO1 in Figure 14. Many factors influence the effect and
magnitude of the direct coupling including: the position of the
LED current setting resistor and the value of the capacitor at
the optocoupler output (CL).
Figure 14 Optocoupler Input to Output Capacitance Model for
Shielded Optocouplers
1 CLEDP
2
6
CLED01
5
3 CLEDN
SHIELD
4
CMR With The LED On (CMRL)
A high CMR LED drive circuit must keep the LED on during
common mode transients. This is achieved by overdriving the
LED current beyond the input threshold so that it is not pulled
below the threshold during a transient. The recommended
minimum LED current of 10 mA provides adequate margin
over the maximum ITH of 4.0 mA (see Figure 1) to achieve
15 kV/μs CMR.
The placement of the LED current setting resistor effects the
ability of the drive circuit to keep the LED on during transients
and interacts with the direct coupling to the optocoupler
output. For example, the LED resistor in Figure 15 is connected
to the anode. Figure 16 shows the AC equivalent circuit for
Figure 15 during common mode transients. During a +dVCM/dt
in Figure 16, the current available at the LED anode (Itotal) is
limited by the series resistor. The LED current (IF) is reduced
from its DC value by an amount equal to the current that flows
through CLEDP and CLEDO1. The situation is made worse
because the current through CLEDO1 has the effect of trying to
pull the output high (toward a CMR failure) at the same time
the LED current is being reduced. For this reason, the
recommended LED drive circuit (Figure 12) places the current
setting resistor in series with the LED cathode. Figure 17 is the
AC equivalent circuit for Figure 12 during common mode
Broadcom
- 10 -